Osteoarthritis Treatment
We Can Recommend the Right Treatment for Your Needs
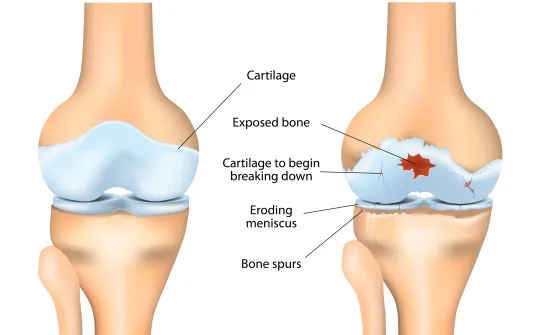
Cartilage covers the end of each bone, creating a smooth surface that allows joints to move easily. But that all-important rubbery cartilage can wear away over time, resulting in pain and swelling in the joints. Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease caused by the loss of cartilage in the joints, making it painful to move your hands, hips, or knees.
If conventional osteoarthritis treatments such as prescription medications, physical therapy, or injections do not provide relief, our doctors at Orthopaedic Specialists of Austin can perform bone realignment or joint replacement surgery. Our practice, with offices in Leander, Lakeland, and Austin, TX, can recommend the right treatment for your needs.

Non-surgical Treatments
There is no known cure for osteoarthritis. However, a wide range of treatments are available to successfully manage symptoms:

Surgery
Not every osteoarthritis patient is a candidate for joint surgery. However, if your doctor recommends surgery, this option can repair or replace compromised joints such as the hips and knees. Drs. David Dodgin and Matthew Heinrich specialize in joint replacement using minimally invasive techniques resulting in a short recovery period and fast healing.
Medicine
Certain medications are also effective for osteoarthritis pain. These include:
- Over-the-counter drugs prescribed by a doctor
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), ranging from aspirin and ibuprofen to prescription drugs, to reduce inflammation and pain
- Corticosteroids, which are anti-inflammatory remedies that can be taken orally or injected directly into a joint
Assistive devices can also help an osteoarthritis patient regain mobility and independence. Scooters, canes, walkers, braces and shoe orthotics are just a few of the devices that patients use to enhance day-to-day living.
Causes & Risk Factors
You may be more likely to develop osteoarthritis if you:

Are Older

Have Inherited Traits That Cause Osteoarthritis
Such as bones that do not fit together normally or an abnormally low production of collagen

Are Overweight
Which stresses joints and causes cartilage to break down quickly

Have Joint Injuries
Including fractures or ligament tears, or engage in an occupation or sport that requires frequent repetitive movements




